Targeting protease nexin-1, a natural anticoagulant serpin, to control bleeding and improve hemostasis in hemophilia
Aymonnier K, Kawecki C, Venisse L, Boulaftali Y, Christophe OD, Lenting PJ, Arocas V, de Raucourt E, Denis CV, Bouton MC
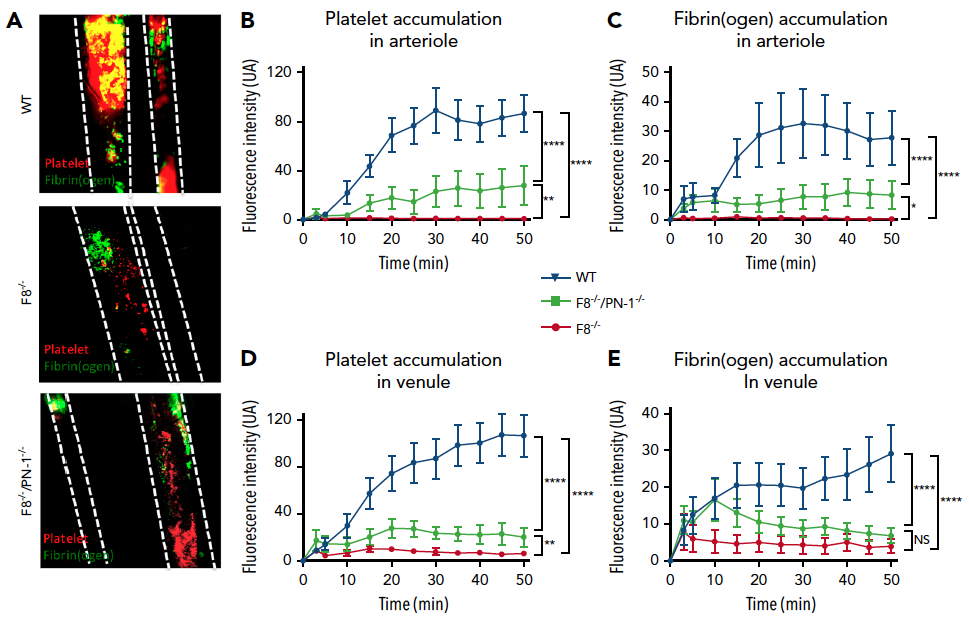
Hemophilia A and B, diseases caused by the lack of factor VIII (FVIII) and factor IX (FIX) respectively, lead to insufficient thrombin production, and therefore to bleeding. New therapeutic strategies for hemophilia treatment that do not rely on clotting factor replacement, but imply the neutralization of natural anticoagulant proteins, have recently emerged. We propose an innovative approach consisting of targeting a natural and potent thrombin inhibitor, expressed by platelets, called protease nexin-1 (PN-1). By using the calibrated automated thrombin generation assay, we showed that a PN-1-neutralizing antibody could significantly shorten the thrombin burst in response to tissue factor in platelet-rich plasma (PRP) from patients with mild or moderate hemophilia. In contrast, in PRP from patients with severe hemophilia, PN-1 neutralization did not improve thrombin generation. However, after collagen-induced platelet activation, PN-1 deficiency in F8-/-mice or PN-1 blocking in patients with severe disease led to a significantly improved thrombin production in PRP, underlining the regulatory role of PN-1 released from platelet granules. In various bleeding models, F8-/-/PN-1-/- mice displayed significantly reduced blood loss and bleeding time compared with F8-/-mice. Moreover, platelet recruitment and fibrin(ogen) accumulation were significantly higher in F8-/-/PN-1-/- mice than in F8-/-mice in the ferric chloride-induced mesenteric vessel injury model. Thromboelastometry studies showed enhanced clot stability and lengthened clot lysis time in blood from F8-/-/PN-1-/- and from patients with hemophilia A incubated with a PN-1-neutralizing antibody compared with their respective controls. Our study thus provides proof of concept that PN-1 neutralization can be a novel approach for future clinical care in hemophilia.

