Prevalence of Systemic Atherosclerosis Burdens and Overlapping Stroke Etiologies and Their Associations With Long-term Vascular Prognosis in Stroke With Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease
Hoshino T, Sissani L, Labreuche J, Ducrocq G, Lavallee PC, Meseguer E, Guidoux C, Cabrejo L, Hobeanu C, Gongora-Rivera F, Touboul PJ, Steg PG, Amarenco P, Investigators A
2017 • JAMA Neurol • [pdf]
 Importance
Importance
: Patients who have experienced stroke with intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD) may also have concomitant atherosclerosis in different arterial beds and other possible causes for ischemic stroke. However, little is known about the frequency and prognostic effect of such overlapping diseases.
Objectives: To describe the prevalence of systemic atherosclerotic burdens and overlapping stroke etiologies and their contributions to long-term prognoses among patients who have experienced stroke with ICAD.
Design, Setting, and Participants: The Asymptomatic Myocardial Ischemia in Stroke and Atherosclerotic Disease study is a single-center prospective study in which 405 patients with acute ischemic stroke within 10 days of onset were consecutively enrolled between June 2005 and December 2008 and followed up for 4 years. After excluding 2 patients because of incomplete investigations, 403 were included in this analysis.
Main Outcomes and Measures: Significant ICAD was defined as having 50% or greater stenosis/occlusion by contrast-enhanced/time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography, computed tomography angiography, and/or transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Systemic vascular investigations on atherosclerotic disease were performed with ultrasonography in carotid arteries, aorta and femoral arteries, and by angiography in coronary arteries. Coexistent stroke etiologies were assessed using the atherosclerosis, small-vessel disease, cardiac pathology, other cause, and dissection (ASCOD) grading system. We estimated the 4-year risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including vascular death, nonfatal cardiac events, nonfatal stroke, and major peripheral arterial events.
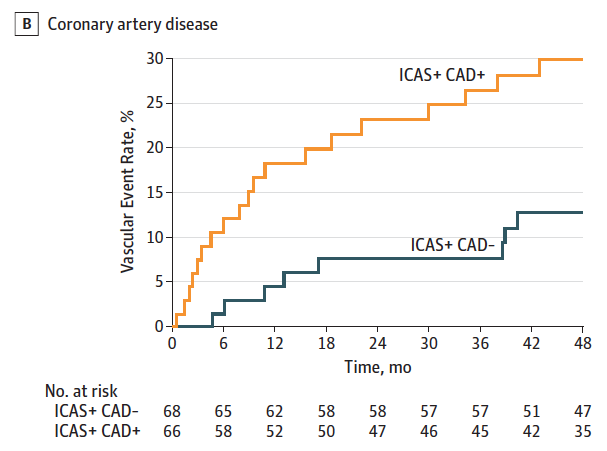
Results: Of 403 participants, 298 (74%) were men and the mean (SD) age was 62.6 (13.1) years. Significant ICAD was found in 146 (36.2%). Patients with significant ICAD more often had aortic arch (70 [60.9%] vs 99 [49.0%]; P = .04) and coronary artery (103 [76.9%] vs 153 [63.2%]; P = .007) atherosclerosis than those without. Among patients with ICAD, concurrent stenosis in the extracranial carotid artery (24 [23.4%] vs 3 [9.0%]; P = .08; adjusted hazard ratio[aHR] = 2.12) and the coronary artery (19 [29.9%] vs 8 [12.8%]; P = .01; aHR = 1.90) increased the MACE risk. Furthermore, patients with ICAD who also had any cardiac pathology (ASCOD grade C1-3) were at a higher MACE risk than others (grade C0) (20 [28.2%] vs 7 [11.4%]; P = .01; aHR = 2.24). By contrast, patients with ICAD with any form of small vessel disease (grade S1-3) had a lower MACE risk than those without (grade S0) (20 [17.3%] vs 6 [34.6%]; P = .05; aHR = 0.23).
Conclusions and Relevance: Patients with ICAD often have coexisting systemic atherosclerosis and multiple potential stroke mechanisms that affect their prognosis, suggesting that extensive evaluations of overlapping diseases may allow better risk stratification.

